Initial conditions#
Perturbations#
When performing a numerical simulation studying the onset of instabilities in a time-dependent problem, it is typical to set for the initial conditions
\[u(\textbf{x}, t=0) = u_0(\textbf{x})=b(\textbf{x}) + \mathcal{N}(\textbf{x})\]
\[\min_{\textbf{x}}\mathcal{N}(\textbf{x}) = \varepsilon^-\]
\[\max_{\textbf{x}}\mathcal{N}(\textbf{x}) = \varepsilon^+\]
When adding some numerical noise \(\mathcal{N}(\textbf{x})\) to the base state \(b(\textbf{x})\), it is desirable to have control of both its amplitude and ‘coarseness’ or frequency.
import numpy as np
from dolfinx.fem import FunctionSpace
from lucifex.mesh import rectangle_mesh, interval_mesh
from lucifex.utils import SpatialPerturbation, DofsPerturbation, sinusoid_noise, cubic_noise, cross_section
from lucifex.viz import plot_line, plot_colormap
Examples: \(d=1\) interval#
\[\Omega = [0, L_x]\]
\[b(x)= 1 - x\]
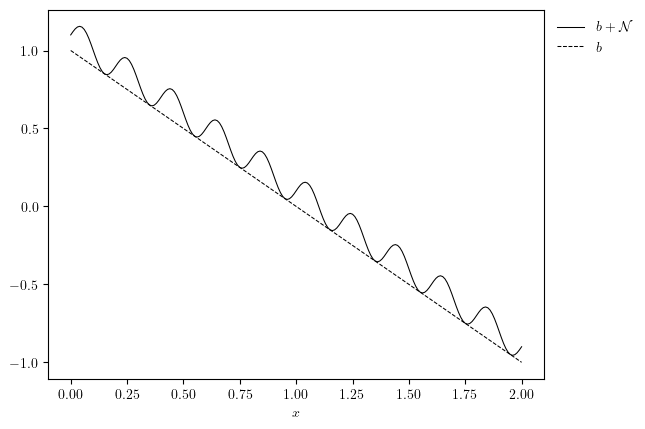
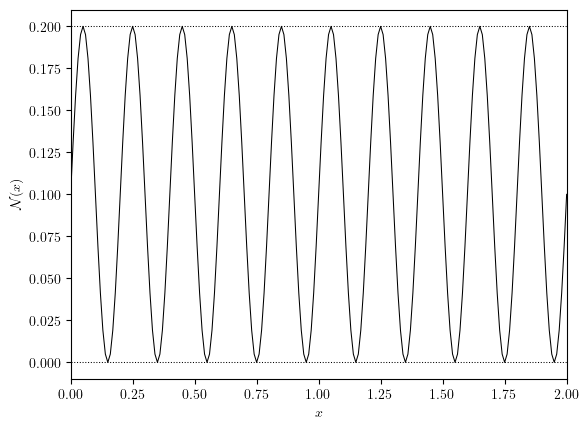
sinusoid noise with specified frequency and subject to periodic boundary conditions
\[\mathcal{N}(x)=\mathcal{N}_{\text{sinu}}(x;n_{\text{waves}})\]
\[ \mathcal{N}_{\text{sinu}}(x=0)=\mathcal{N}_{\text{sinu}}(x=L_x)=0\]
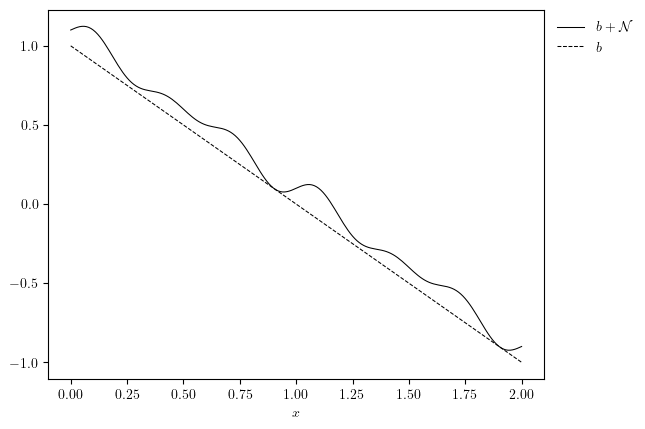
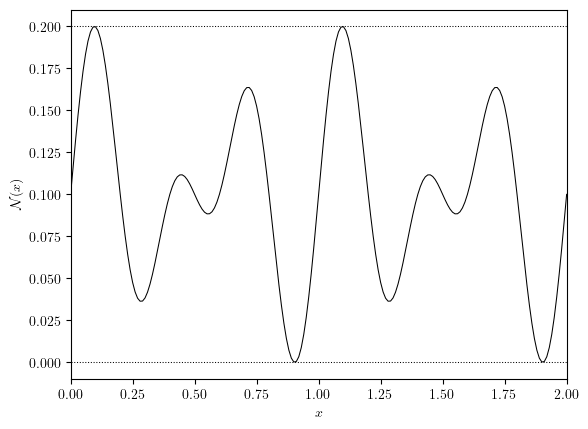
prescribed noise function
\[\mathcal{N}(x;\lambda_0, \lambda_1)=\cos(2\pi x/\lambda_0)\sin(2\pi x/\lambda_1)\]
Lx = 2.0
mesh = interval_mesh(Lx, 200)
fs = FunctionSpace(mesh, ('P', 1))
n_waves = 10
sinu_noise = sinusoid_noise('periodic', Lx, n_waves, 0)
lmbda = (Lx, 0.2 * Lx)
sincos_noise = lambda x: np.cos(2* np.pi * x[0] / lmbda[0]) * np.sin(2 * np.pi * x[0] / lmbda[1])
for noise in (sinu_noise, sincos_noise):
eps = 0.2
perturbation = SpatialPerturbation(
lambda x: 1 - x[0],
noise,
[Lx],
eps,
)
u0 = perturbation.combine_base_noise(fs)
uBase = perturbation.base(fs)
uNoise = perturbation.noise(fs)
plot_line([u0, uBase], x_label='$x$', legend_labels=['$u_0=b+\mathcal{N}$', '$b$'])
fig, ax = plot_line(uNoise, x_label='$x$', y_label='$\mathcal{N}(x)$')
ax.hlines((0, eps), 0, Lx, colors='black', linestyles='dotted', linewidths=0.75)
Examples: \(d=2\) rectangle#
\[\Omega = [0, L_x]\times[0, L_y]\]
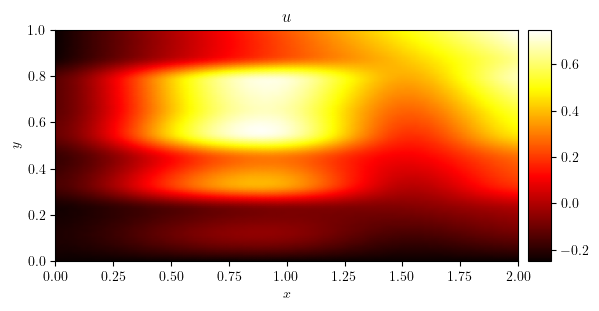
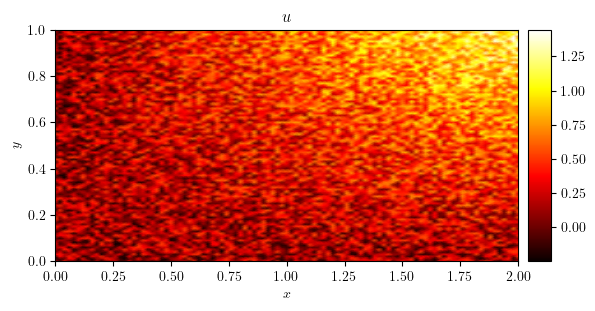
\[b(x, y)= \tfrac{1}{2}xy\]
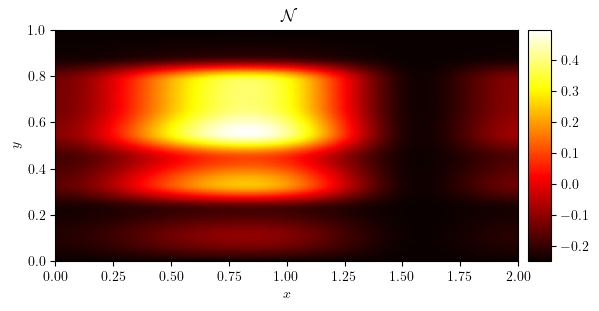
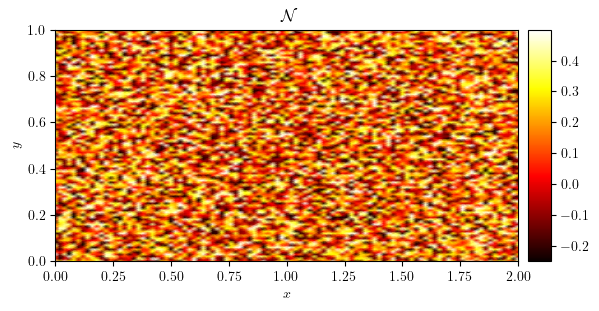
cubic interpolation noise with specified frequency and subject to Neumann/Dirichlet boundary conditions
\[\mathcal{N}(x)=\mathcal{N}_{\text{cubi}}(x;n_{\text{freq}})\]
\[\frac{\partial\mathcal{N}_{\text{cubi}}}{\partial x}(x=0,y)=\frac{\partial\mathcal{N}_{\text{cubic}}}{\partial x}(x=L_x,y)=\mathcal{N}_{\text{cubi}}(x,y=0)=\mathcal{N}_{\text{cubic}}(x,y=L_y)=0\]
degrees-of-freedom vector noise
\[\textbf{u}_0 = \textbf{b} + \textbf{N}\quad\text{where}\quad u_0(\textbf{x})=\sum_ju_{0,j}\xi_j(\textbf{x})\]
Lx = 2.0
Ly = 1.0
mesh = rectangle_mesh(Lx, Ly, 100, 100)
fs = FunctionSpace(mesh, ('P', 1))
base = lambda x: 0.5 * x[0] * x[1]
eps = (-0.25, 0.5)
freq = (5, 10)
seed = (11, 22)
noise_perturbation = SpatialPerturbation(
base,
cubic_noise(['neumann', 'dirichlet'], [Lx, Ly], freq, seed, (0, 1)),
[Lx, Ly],
eps,
)
dofs_perturbation = DofsPerturbation(
base,
123,
eps,
)
for perturbation in (noise_perturbation, dofs_perturbation):
u0 = perturbation.combine_base_noise(fs)
uBase = perturbation.base(fs)
uNoise = perturbation.noise(fs)
print(f'min(N) = {min(uNoise.x.array)}')
print(f'max(N) = {max(uNoise.x.array)}')
plot_colormap(u0, title='$u_0$')
plot_colormap(uNoise, title='$\mathcal{N}$')
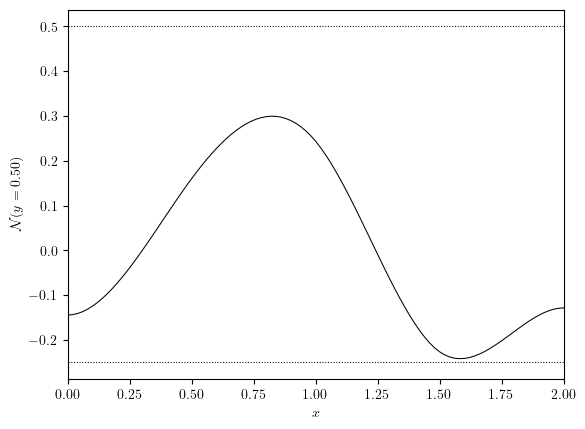
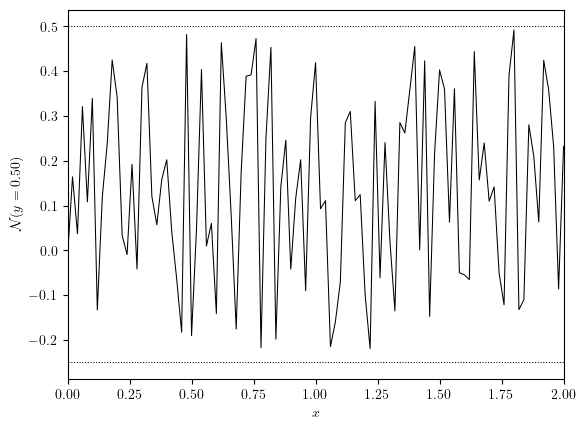
x_axis, uNoise_x, y_value = cross_section(uNoise, 'y', 0.5)
fig, ax = plot_line((x_axis, uNoise_x), x_label='$x$', y_label=f'$\mathcal{{N}}(y={y_value:.2f})$')
ax.hlines(eps, 0, Lx, colors='black', linestyles='dotted', linewidths=0.75)
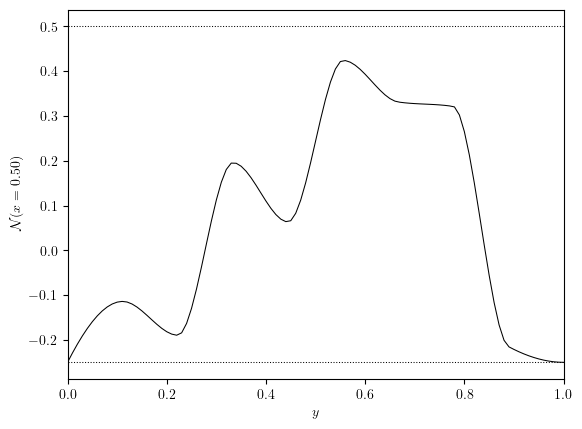
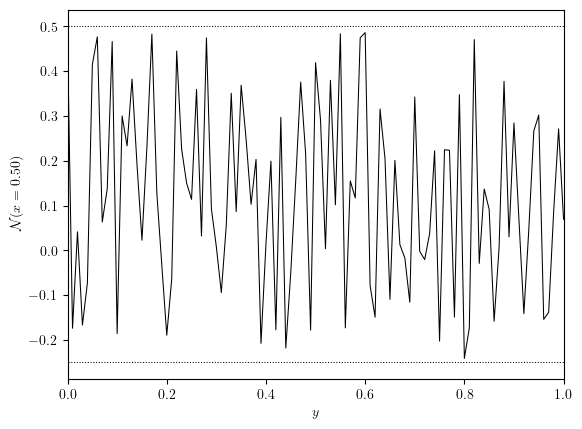
y_axis, uNoise_y, x_value = cross_section(uNoise, 'x', 0.5)
fig, ax = plot_line((y_axis, uNoise_y), x_label='$y$', y_label=f'$\mathcal{{N}}(x={y_value:.2f})$')
ax.hlines(eps, 0, Lx, colors='black', linestyles='dotted', linewidths=0.75)
min(N) = -0.25
max(N) = 0.4994233082812214
min(N) = -0.2499879345102143
max(N) = 0.49996212192760614
The Kernel crashed while executing code in the current cell or a previous cell.
Please review the code in the cell(s) to identify a possible cause of the failure.
Click <a href='https://aka.ms/vscodeJupyterKernelCrash'>here</a> for more info.
View Jupyter <a href='command:jupyter.viewOutput'>log</a> for further details.